Cellular connectivity is on the verge of getting a major overhaul with the imminent launch of 5G networks and 5G smartphones.
5G connectivity is much, much faster than 4G LTE, which means in just a few years, we’re going to be seeing far faster connection speeds on our devices. 5G technology is coming to both mobile and home networks, with rollouts happening starting in 2019.
5G iPhone Launch Date
Multiple rumors dating back months have suggested Apple is going to launch a 5G iPhone in 2020, which means the 2019 iPhones will continue to use 4G.
There were questions about whether Apple would be able to secure 5G chips for its 2020 devices given its dispute with Qualcomm, but that litigation has been cleared up and the road to a 5G iPhone in 2020 is clear.
Apple won’t be prepared to launch 5G iPhones in 2019 and can’t afford to wait until 2021 as competitors are already launching 5G smartphones, which makes 2020 Apple’s 5G year.
5G Explained
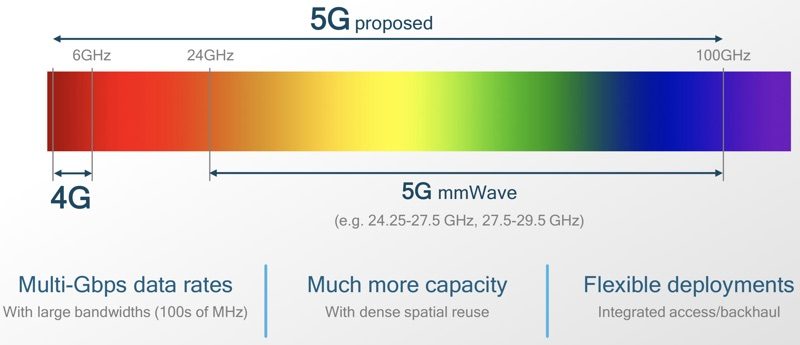
5G is fifth-generation cellular wireless and the successor to 4G. When most people talk about 5G connectivity, they’re talking about mmWave, or millimeter wave spectrum.
Millimeter wave technology offers a lot of open bandwidth for blazing fast data transfer speeds, but it is highly sensitive to interference from buildings, trees, and other obstacles, which has prevented it from being taken advantage of by cellular companies who have previously focused on low-band and mid-band spectrums for cellular networks.
Accessing mmWave spectrum has only become possible over the course of the last few years due to technological advancements like Massive MIMO, adaptable beamforming, and miniaturization of complex antenna processing functions.
Not all 5G networks are going to use mmWave technology in all areas because it’s best suited to denser urban locations. In rural and suburban areas, 5G technology will be on mid-bands and low-bands, called sub-6GHz 5G. It’s still faster than 4G, but not as fast as mmWave.
So when 5G comes out, there will be some areas with mmWave technology where data transfer speeds will be lightning quick, coupled with other areas that are closer to 4G LTE speeds. Over time, low-band and mid-band 5G speeds should also get much quicker, but know that most talk of 5G focuses on the more limited mmWave spectrum.
5G Benefits
5G is going to provide faster connection speeds on cellular and home internet devices. How much faster remains to be seen because 5G networks are not widespread yet and are just now starting to be built out by carriers in the United States.
As mentioned above, there are also different implementations of 5G that are going to impact how fast a 5G network is, but in a nutshell, it’s going to make data connections faster and more robust.
5G Drawbacks
It will take time for 5G technology to roll out, and a lot of the fastest 5G speeds will be limited to major cities as carriers work to build out their networks and upgrade their equipment.
For the first few years after launch, 5G connectivity will be spotty with carriers relying on LTE as a backup. Early 5G devices will eat up a lot of battery, which is something that will get better with the second-generation 5G chips Apple is likely to use.
U.S. Carriers With 5G Networks
All four of the major carriers in the United States – Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, and Sprint – are working on 5G technology, with 5G networks rolling out starting in 2019. Other carriers around the world are also developing 5G networks. All of the U.S. carriers are promising maximum connectivity speeds 10 to 20 times faster than LTE.
Verizon – Verizon has launched its 5G LTE network in areas in Chicago and Minneapolis, with plans to expand to 30 more cities in 2019. Verizon is focusing heavily on mmWave spectrum.
AT&T – AT&T is confusingly labeling its 5G networks in multiple ways, calling its upgraded 4G LTE "5GE" and its mmWave coverage "5G+." 5G+ is AT&T’s real, actual 5G mmWave network, and it is available in select areas in cities that include Los Angeles, Orlando, Atlanta, Raleigh, Indianapolis, Austin, and more.
T-Mobile – T-Mobile is taking a practical approach to 5G and is focusing on the 600MHz spectrum first, because that’s what most customers will connect to. As mentioned up above, this spectrum is faster than LTE but slower than mmWave, and will provide better coverage. T-Mobile says it plans to start rolling out 5G in 2019.
Sprint – Sprint’s 5G plans are tied to T-Mobile, because of T-Mobile’s Sprint purchase. The merger between the two companies is not complete, but both companies are counting on it being finished in the first half of the year. That said, Sprint is planning to roll out 5G connectivity in May in Chicago, Atlanta, Dallas, and Kansas City. Sprint does not have licensing for mmWave technology and its 5G will be focused on mid-band spectrum.
Apple’s Chip Partner – Qualcomm
Apple was originally planning to use Intel chips in its 2020 5G iPhones, but Intel is out of the smartphone chip business and Apple has no choice but to use Qualcomm’s modem chips.

Qualcomm has already released one 5G chip, the X50, and is working on a second, the X55. Qualcomm’s X55 chip will be available later in 2019, and could be the modem chip Apple will use in its 2020 iPhones.
The X55 offers 7Gb/s peak download speeds and 3Gb/s upload speeds, though these numbers are theoretical maximums and actual speeds will depend on carrier network. This chip is Qualcomm’s first 5G chip that supports all major frequency bands, operation modes, and network deployments.
The X55 is also more power efficient than Qualcomm’s X50 chip, which means it will draw less energy and will have less of an impact on battery life when connected to a 5G network.
Guide Feedback
Have questions about the 5G iPhone or want to offer feedback on this guide? Send us an email here.
This article, "Apple’s 2020 5G iPhone" first appeared on MacRumors.com
Discuss this article in our forums






Recent Comments